Home >>DBMS Tutorial >DBMS File Structure
DBMS File Structure
DBMS File Structure
Relative knowledge and data is collectively stored in file formats. A file is a record sequence that is stored in binary format. A disk drive that can store records is formatted into several blocks. On such disk blocks, file records are mapped.
File Organization
File Organization determines how records of files are mapped to blocks of disks. To organize file records, we have four types of file Organization:
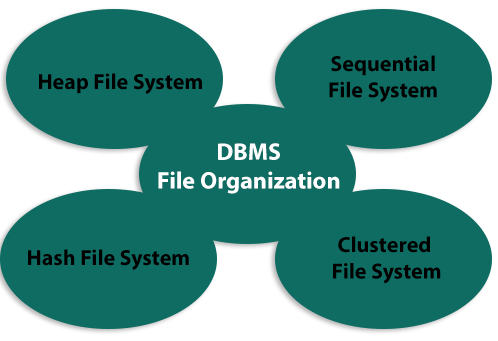
Heap File Organization
When a file is created using Heap File Organization, without any specific accounting details, the Operating System allocates the memory area to that file. Anywhere in that memory area, file records can be placed. The software is responsible for managing the records. Any ordering, sequencing or indexing on its own is not supported by Heap File.
Sequential File Organization
Every record of a file contains a data field (attribute) to define the record uniquely. Records are put in the file in a sequential order in the sequential file organization, based on the specific key field or search key. Practically, it is not possible to store all records in physical form sequentially.
Hash File Organization
The Hash File Organization uses certain fields of the records to compute the Hash function. The hash function output specifies the location of the disk block where the records should be stored.
Clustered File Organization
The organization of clustered data is not considered good for large databases. Linked records from one or more relations are kept in the same disk block in this mechanism , i.e., record ordering is not based on a primary key or search key.
File Operations
Database file operations can be divided broadly into two categories:
- Update Operations
- Retrieval Operations
Update operations alter the values of data by inserting , deleting, or updating them. On the other hand, retrieval operations do not change the data, but retrieve it after optional conditional filtering. Selection plays a major role in all kinds of operations. There may be other operations, other than creating and deleting a file, that can be performed on files.
- Open −One of the two modes, read mode or write mode, will open a file. The operating system does not allow someone to change data in the read mode. Data, in other words, is read only. It is possible to share files opened in read mode between many entities. Write Mode allows modification of data. It is possible to read files opened in write mode but can not be exchanged.
- Locate-Each file has a file pointer that tells the current location where to read or write the files. It is able to adjust this pointer accordingly. It can be moved forward or backward using a find (seek) operation.
- Read −By example, the file pointer points to the beginning of the file when files are opened in the read mode. There are options where the user can tell the operating system at the moment of opening a file where to find the file pointer. It will read the very next data to the file pointer.
- Write- The user may choose to open a file in write mode, allowing them to modify its contents. It can be deleted, inserted or modified. The file pointer can be located at the time of opening, or can be modified dynamically if it is allowed to do so by the operating system.
- Close —This is the most significant process from the viewpoint of the operating system. The operating system when a request to close a file is generated
- Removes (if in shared mode) all locks,
- Save the data to the secondary storage media (if altered) and
- It releases all the file-related buffers and file handlers.
