Home >>DBMS Tutorial >DBMS ER Model Basic Concepts
DBMS ER Model Basic Concepts
DBMS ER Model Basic Concepts
The ER model describes a database's conceptual view. It revolves around people in the real world and the associations between them. The ER model is considered to be a good option for designing databases at the viewpoint level.
Entity
An entity may be an easily identifiable real-world object, either animate or inanimate. For instance, students , teachers, classes, and courses offered may be considered as entities in a school database. There are certain attributes or properties of all these entities that give them their identity.
A collection of similar types of entities is an entity set. An entity set can contain entities with similar values sharing an attribute. For example, a set of students may contain all of a school's students; likewise, a set of teachers may contain all of a school's teachers from all staff. Entity sets do not have to be disjointed.
Attributes
Entities are represented, called attributes, by means of their properties. The attributes all have meanings. A student entity, for example, may have attributes such as name, class , and age.
A domain or value set exists that can be assigned to attributes. The name of a student, for example, should not be a real number. It's got to at least be alphabetic. The age of a student can not be negative, etc.
Types of Attributes
These types of characteristics can come together in a way like—
- Simple attribute-Simple attributes are atomic values that are not more separable. For example, a student's phone number is a 10-digit atomic value.
- Composite attribute-More than one basic attribute is made of composite attributes. For example, the full name of a student can have a first and last name.
- Derived attributes-attributes are attributes that do not exist in the physical database, but their values are derived from other attributes that are present in the database. Average salaries in a department , for example, should not be stored directly in the database, but can be extracted instead. Another example is that age can be extracted from birth data.
- Single-value attributes:-are single-value attributes. Social Security-Number, for example.
- Multi-value attribute-Multi-value attributes are allowed to have more than one value. A person may have more than one phone number, email address, etc., for instance.
- Easy attributes with a single-value
- Easy attributes with multiple values
- Single-value composite attributes
- Multi-valued composite attributes
Entity-Set and Keys
Key is an attribute or attribute collection that defines an entity uniquely within the set of entities.
For instance, a student's roll_number makes it identifiable among students.
- Super Key: A set of attributes (one or more) that in an entity set collectively defines an entity.
- Candidate Key:A candidate key is considered a minimal super key. More than one candidate key can be used for an entity set.
- Primary Key: One of the candidate keys chosen by the database designer to define the entity set uniquely is a primary key.
Relationship
The association between entities is called a relationship. An employee works in a department , for example, and a student enlists in a course. Here, relationships are called Works at and Enrolls.
Relationship Set
A relationship set is called a set of relationships of a similar type. Like entities, there can be attributes in a relationship too. The descriptive attributes are called these attributes.
Degree of Relationship
In a relationship, the number of participating entities defines the degree of the relationship.
- Binary = degree 2
- Ternary = degree 3
- n-ary = degree
Mapping Cardinalities
Cardinalitydetermines the number of entities in one set of entities which, by means of a set of relationships, may be associated with the number of entities in an another set.


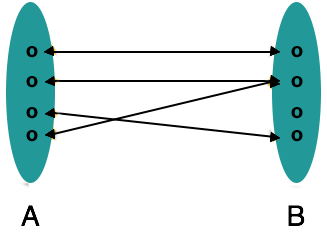
Many-to-many-One entity from A may be associated with more than one entity from B and vice versa.
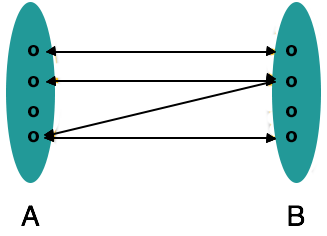
- One-to-one-One entity from set A entity can be associated to at most one set B entity and vice versa.
- One-to-many-One entity from entity set A may be associated with more than one entity set B, but at most one entity can be associated with an entity from entity set B.
- Many-to-one − More than one entity from entity set A can be associated with at most one entity from entity set B, but more than one entity from entity set A can be associated with an entity from entity set B.
