Home >>DBMS Tutorial >DBMS Data Schemas
DBMS Data Schemas
DBMS Data Schemas
Database Schema
The skeleton structure which represents the logical view of the whole database is a database schema. It determines how the data is structured and how the relations between them are related. It formulates all of the limitations to be applied to the data.
The schema of a database defines its entities and the relationship between them. This includes a detailed description of the database, which can be shown by means of schema diagrams. It is the designers of the database who design the schema to help programmers understand and make the database useful.
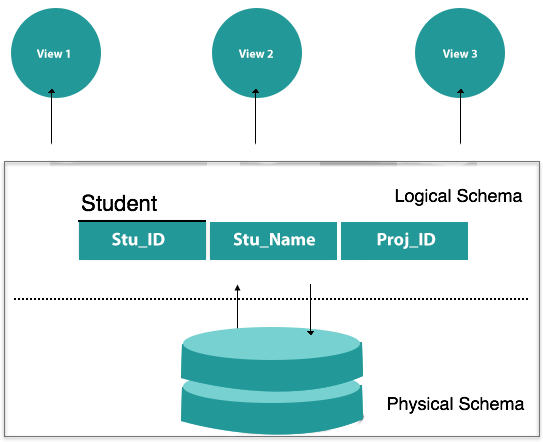
You may broadly divide a database schema into two categories.
- Physical Database Schema -This schema applies to the actual data storage and its storage form, such as files, indices, etc. It determines how in secondary storage the data will be stored.
- Logical database schema- This schema explains all the logical limitations that must be applied to the stored data. It describes tables, opinions, and constraints of integrity.
Database Instance
It is important that we individually separate these two terms. The database schema is a database skeleton. When the database does not exist at all, it is designed. If the database is working, any improvements to it are very difficult to make. No data or information is contained in a database schema.
A database example is an operating database state with data at any given time. It includes a database snapshot. Instances in the database tend to change over time. A DBMS guarantees that each instance (state) is in a correct state by diligently following all the validations, limitations, and conditions imposed by the database designers.
