Home >>DBMS Tutorial >DBMS Architecture
DBMS Architecture
DBMS Architecture
A DBMS design is based on its architecture. It can be hierarchical or hierarchical or centralized. It is possible to see the architecture of a DBMS as either single or multi-tier. The n-tier architecture divides the entire system into n modules that are related but separate, which can be modified, changed, modified or replaced independently.
The DBMS is the only entity in a 1-tier architecture where the user sits directly on the DBMS and uses it. Any improvements made here will be carried out on the DBMS itself directly. For end-users, it does not have handy tools. Designers and programmers of databases usually prefer to use a single-tier architecture.
If the DBMS architecture is 2-tier, it must provide an application by which to access the DBMS. Programmers use a 2-tier architecture where, via an application, they access the DBMS. Here, in terms of operation, design and programming, the application tier is totally independent of the database.
3-Tier Architecture
Based on the complexity of the users and how they use the data present in the database, a 3-tier architecture divides the tiers from each other. It is the architecture most commonly used to design a DBMS.
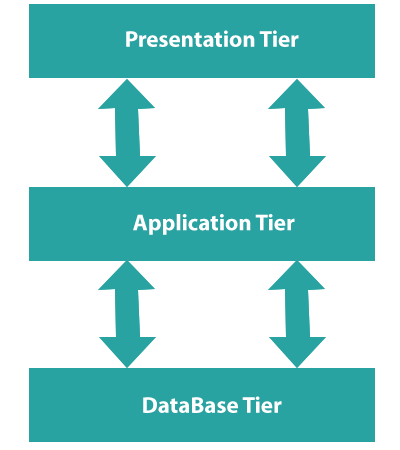
- Database (Data) Tier − The database resides at this level along with its query processing languages. At this level, we also have the relationships that define the data and their constraints.
- Application (Middle) Tier − The application server and the applications that access the database reside at this tier. This application tier provides an abstracted database view for a user. End-users are unaware of the database 's presence outside of the application. On the other hand, no other user above the application tier is aware of the database tier. The application layer, therefore, stands in the middle and acts as a mediator between the end-user and the database.
- User (Presentation) Tier - On this tier, end-users work and know little about the existence of the database above that layer. At this layer, the application can provide multiple views of the database. Applications which reside in the application tier generate all views. The architecture of multiple-tier databases is highly modifiable, since almost all its components are independent and can be independently modified.
