Home >>C++ Tutorial >C++ Exception Handling
Exception Handling in C++
C++ Exception Handling
The procedure that is used to handle the runtime errors is known as the exception handling in C++. In order to maintain the normal flow of the application even after the runtime errors, the exception handling is performed in the C++ programming.
The event or object that is thrown at the runtime is known as the exception in C++. The source of all the exceptions from which they are derived is std::exception class. It is basically the runtime error that can be easily handled. The exception message is printed and the program is terminated, in case the exceptions are not handled well.
Advantages of exception handling
The main advantage is that it maintains the normal flow of the application and when it happens the code is executed even after the exception is implemented.
C++ Exception Classes
<exception> class is the class where the standard exceptions are defined in the C++ programming. Here is the hierarchy of parent-child class depicted:
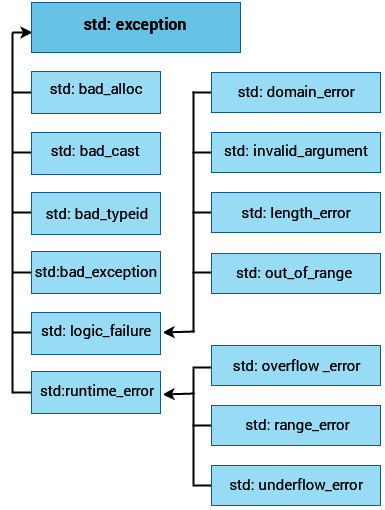
We all knew as a fact that all the exception classes in C++ are basically derived from the std::exception class.
Here is the list of the common exception classes in C++ depicted below:
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| std::exception | This exception is basically an exception and the parent class of all standard C++ exceptions. |
| std::logic_failure | This exception can be detected just by reading a code in the C++. |
| std::runtime_error | This is an exception in C++ that cannot be detected by reading a code. |
| std::bad_exception | This exception in C++ is generally used to handle the unexpected exceptions in a C++ program. |
| std::bad_cast | This exception in C++ is generally known to be thrown by dynamic_cast. |
| std::bad_typeid | This exception in C++ is generally known to be thrown by typeid. |
| std::bad_alloc | This exception in C++ is generally known to be thrown by new. |
